소프트웨어
DIANA
Tunnelling & Underground
DIANA는 터널 프로젝트에서 여러가지 방법으로 활용될 수 있습니다. 해석은 일반적으로 터널 유도 정착이나 라이닝 응력 분석에 초점을 추지만, DIANA는 화재, 폭발 또는 지진 발생 시 터널이 어떻게 반응하는지 연구하는 데에도 사용될 수 있습니다.
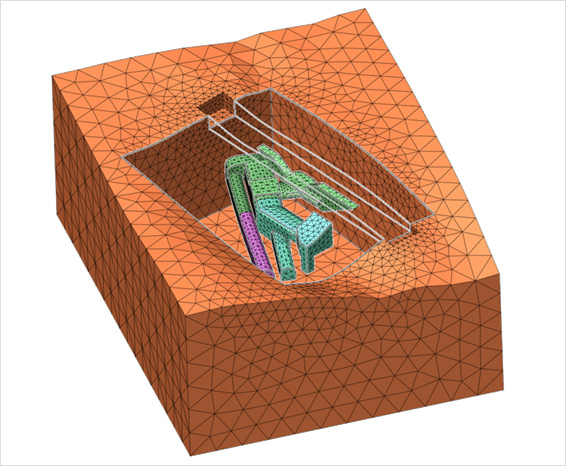
현재, 도시에서 혼잡이 증가함에 따라 기존 구조물에서 터널을 굴착하는 것뿐만 아니라, 기존 터널에서도 터널을 굴착하는 지하 운송 시스템으로 전환하고 있습니다. 지반의 이동은 이접 구조물에 불가피한 위험요소이며 계획 단계와 프로젝트 이행 시 주의 깊게 접근되어야 합니다. 이는 건설 안정성과 프로젝트 비용에 잠재적으로 부정적인 영향을 미칠 뿐만 아니라 이러한 예측을 정확하게 할 수 있는 능력이 핵심이라는 것을 의미합니다. 녹지에서의 얕은 터널 건설로 인한 지표침하는 어느 정도 쉽게 예측 가능합니다. 그러나 도시 지역에서의 지표 침하는 터널과 샤프트, 지면 및 건물 사이의 훨씬 복잡한 상호 작용을 보여줍니다.
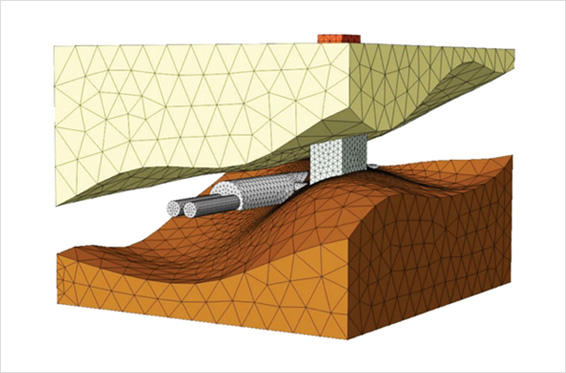
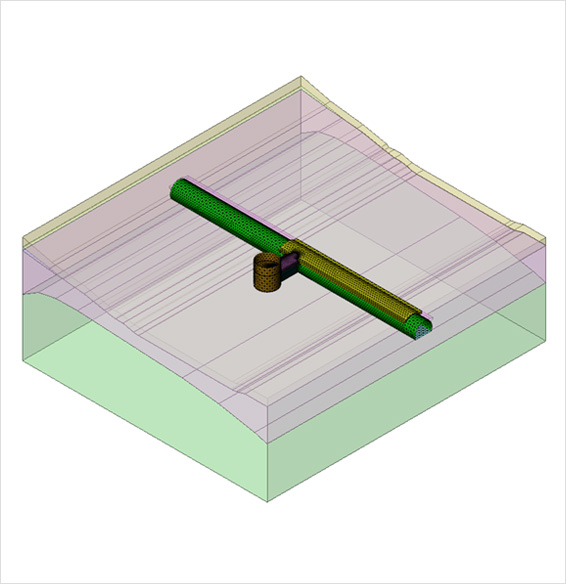
DIANA 프로그램을 사용하여 건물, 지표와 터널 및 샤프트 간의 상호 작용에 대한 상세한 2차원 및 3차원 해석을 수행할 수 있습니다. 구조적 손상, 결빙, 화재, 홍수 또는 지진으로 인한 사고의 영향으로 기존 및 신규 건설되는 터널 라이닝을 분석하는 것은 터널의 안전과 수명에 매우 중요합니다. DIANA로 터널 세그먼트와 그 연결부를 모델링할 수 있으며, 그 위에 지반과 그라우트의 압력을 가하여 잠재된 변형 형상을 확인할 수 있습니다.
- In-situ Stress ( Ko procedure/gravity loading/pre-stress) and Pore-pressure Initialization
- Drained / Undrained Analysis
- Construction-staged analysis
- Seepage analysis (steady state / transient)
- Saturated or Partially Saturated Flow
- Consolidation analysis (full coupled stress-flow analysis)
- Pressure dependent degree of saturation
- Porosity or saturation dependent permeability
- Deformation dependent density and porosity
- Large displacement and large strain nonlinear analysis
- Special elements for nonlinear modeling of joints between the TBM lining segments
- Ground freezing analysis including latent heat consumption, thermal expansion and temperature dependent elasto-plasticity
- Generalized plane strain elements for 2D modeling of inclined tunnels or shafts in strongly anisotropic in-situ stresses
-
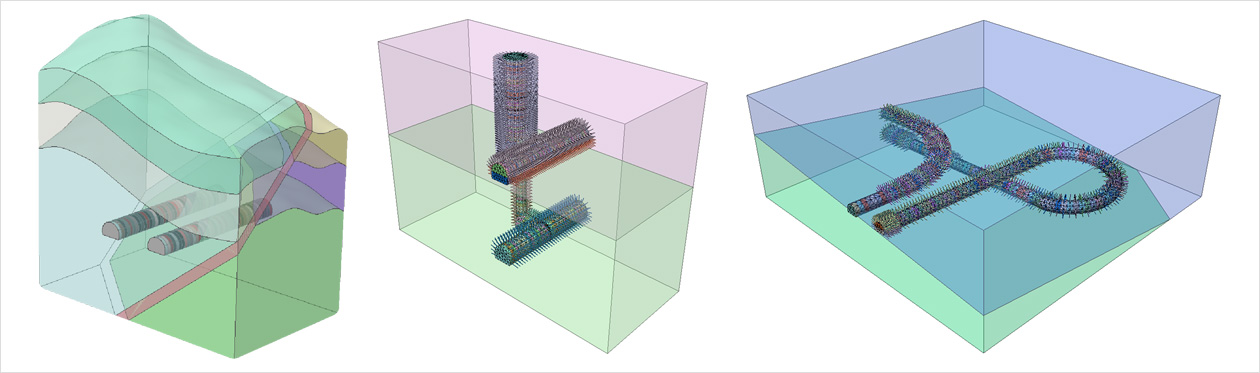
Mesh-independent embedded bars and grids that allow easy modelling of:
- - rock bolts, nails or geotextiles in solid soil elements
- - reinforcement in beam or shell structural elements
- Soil-structure interaction with non-linear behaviour for both soil and structure
- Wide range of material models for the analysis of non-linear concrete material behavior
- Transient nonlinear analysis for viscous behaviour such as creep, shrinkage or swelling, ambient influence such as temperature or chemical concentration
- Young concrete analysis including hydration heat, shrinkage, hardening, visco-elasticity and cracking
- Higher order solid elements up to cubic interpolation
- Eigenvalue analysis (eigenfrequencies, eigenmodes, participation factors, effective masses)
- Direct frequency response analysis
- Modal frequency response analysis
- Spectral response analysis (ABS, SRSS, and CQC modal combinations)
- Linear and nonlinear time domain analysis (total, transient and steady state, solution)
- Various time integration methods, e.g. Newmark, Wilson-theta, Runge-Kutta
- Hybrid Frequency-time domain analysis (steady state solution)
- Fluid-structure interaction
- Multi-directional base acceleration loads
- Prescribed nodal acceleration loads (release summer 2011)
- Distributed mass elements (2D line elements + 3D surface elements)
- Bounding/boundary elements for far field behavior (2D line elements + 3D surface elements)
- Viscous, structural, and continuous damping
- Specified or calculated initial conditions
- Consistent or lumped mass and/or damping matrices
- Towhata-Iai liquefaction model (2D models and largely undrained conditions)
- Nishi liquefaction model (for 2D/3D, partially drained conditions, arbitrary shearing direction)
- Bowl liquefaction model (for 2D/3D, partially drained conditions, horizontal shearing)
- User-supplied liquefaction models (USRLIQ subroutine)