소프트웨어
건설분야 최고의 해석 솔루션 DIANA와 함께 합니다.
DIANA
Young Hardening Concrete
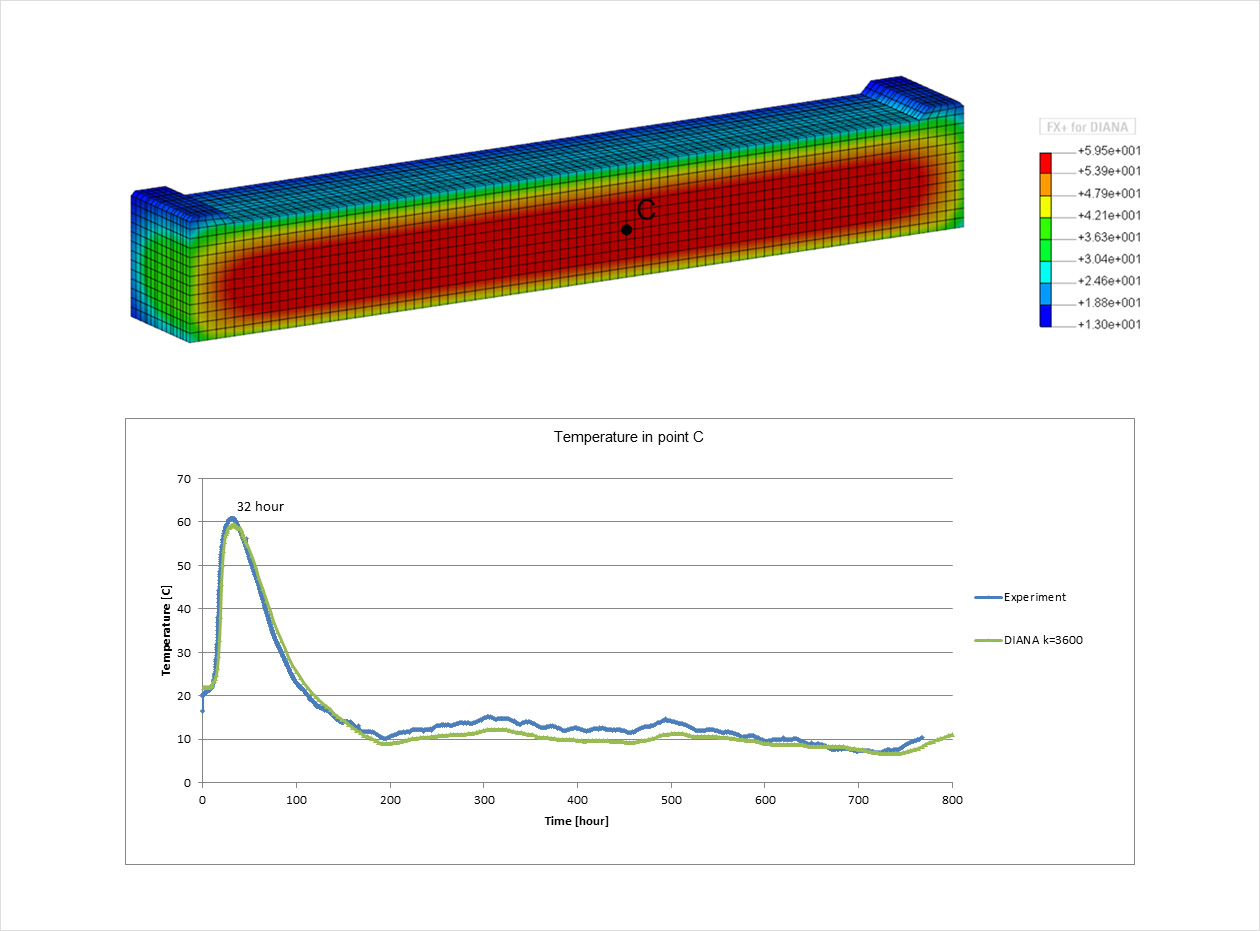
콘크리트 대량 타설은 서비스 수명 이전에 구조물의 조기 균열을 초래할 수 있습니다. 이는 댐과 같은 수력 구조물의 경우에 위험할 수 있습니다. 배합의 선택, 시간과 연속적인 타설은 콘크리트의 균열을 줄이거나 방지할 수 있습니다. 경우에 따라 냉각 시스템을 사용할 수도 있습니다. 초기 재령 콘크리트의 거동은 구조물의 확장이나 보수 등의 목적으로 기존 구조물에 타설하는 경우에도 해당됩니다. DIANA는 다양한 범위의 초기 재령 콘크리트 모델을 제공하며, 선형 또는 보다 상세한 비선형 분석으로 균열을 예측할 수 있습니다.
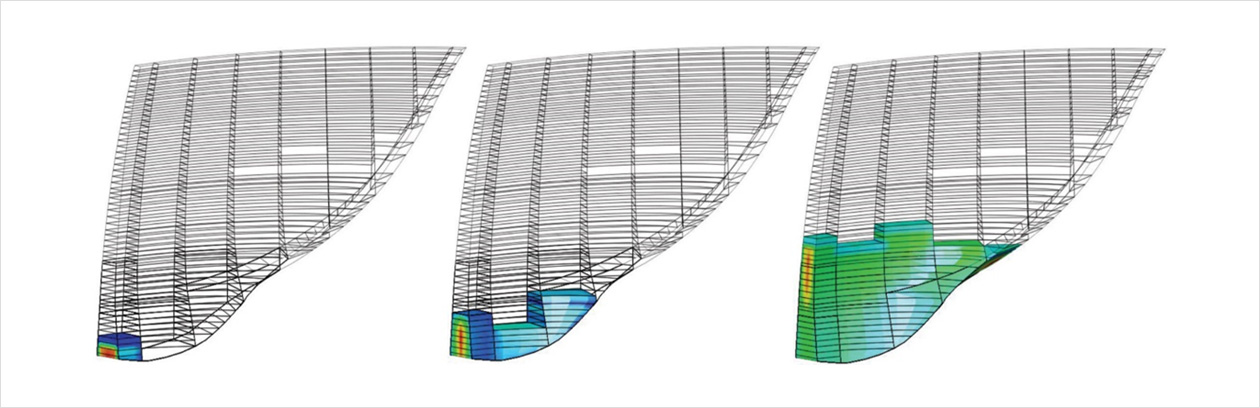
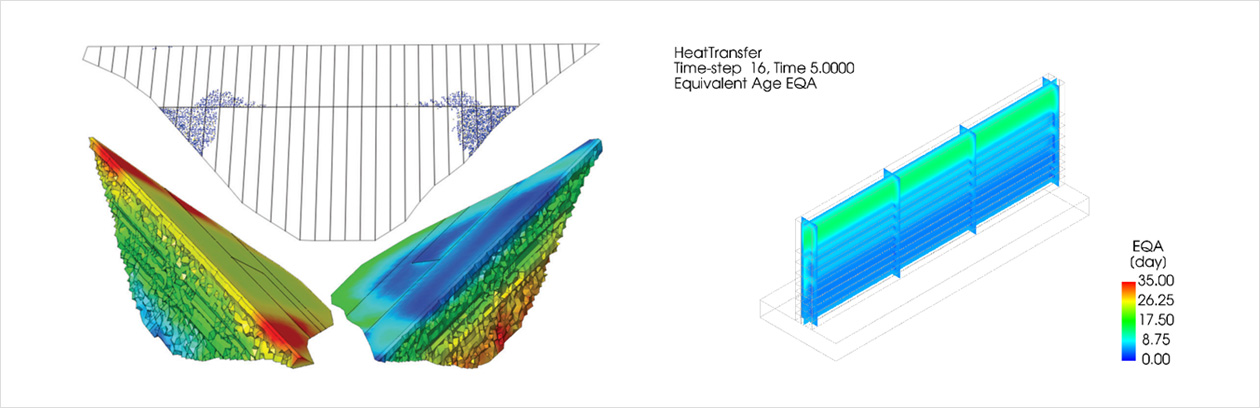
구조물을 초기 재령에 대해서 해석하는 것은 크리프와 건조수축과 같이 구조물의 수명 기간에 다른 문제를 시뮬레이션하는 일련의 분석이 뒤 따릅니다. 이를 통해 구조물의 수명 기간 중 언제든지 스트레스 상태를 보다 현실적으로 모델링하고 구조물의 손상을 유발하거나 구조 성능을 저하시킬 수 있는 결함의 발생을 예측할 수 있습니다.
- Coupled thermo-stress with automatic conversion of temperature field to mechanical loading
- Possibility to add/remove elements or change boundary conditions during the analysis
-
Calculation of the heat of hydration from:
- - Direct input of the heat production as function of the degree of reaction
- - Preprocessing from the adiabatic curve
- - User Supplied Subroutine
- Heat transfer by conduction, convection and radiation
- Dependence of thermal material properties on temperature, time and degree of reaction
- Time dependence of the convective heat coefficient, to simulate presence or removal of scaffolding, and presence of wind
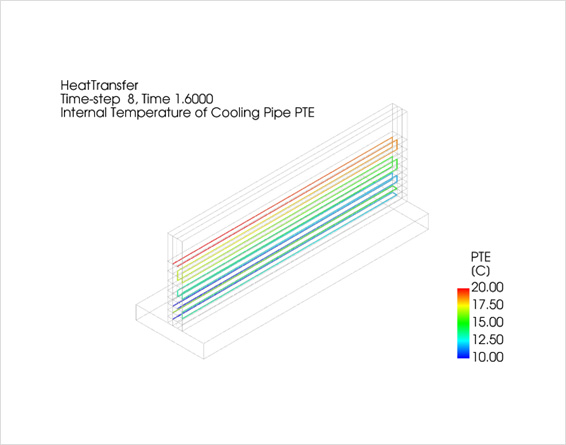
- Cooling pipe elements
재료 모델 (Material Models)
-
Evolution of Young’s modulus according to:
- - Reinhardt model
- - Model codes (CEB-FIP Model Code 1990 & 2010, Eurocode, ACI 209, AASHTO, NEN 6720/A4, JSCE, JCI, KCI)
- - Laboratory curves
- - User Supplied Subroutine
- Visco-elasticity: Double Power Law, Kelvin and Maxwell chains
- Crack prediction with the tensile strength utilization index and degree of reaction dependent tensile strength (linear analysis)
-
Crack prediction with non-linear analysis:
- - Smeared crack models with:
- - Degree of reaction dependence of the tension cut-off and tension softening
- - Degree of reaction dependence of shear behavior
- - Degree of reaction dependence of compression functions
- - Discrete crack model with degree of reaction dependence of the tension cut-off and tension softening
- Visco-elasticity with temperature dependent Young's modulus: Power law, Kelvin and Maxwell chains
- Transient creep
- User-supplied subroutines