소프트웨어
건설분야 최고의 해석 솔루션 DIANA와 함께 합니다.
DIANA
Fire
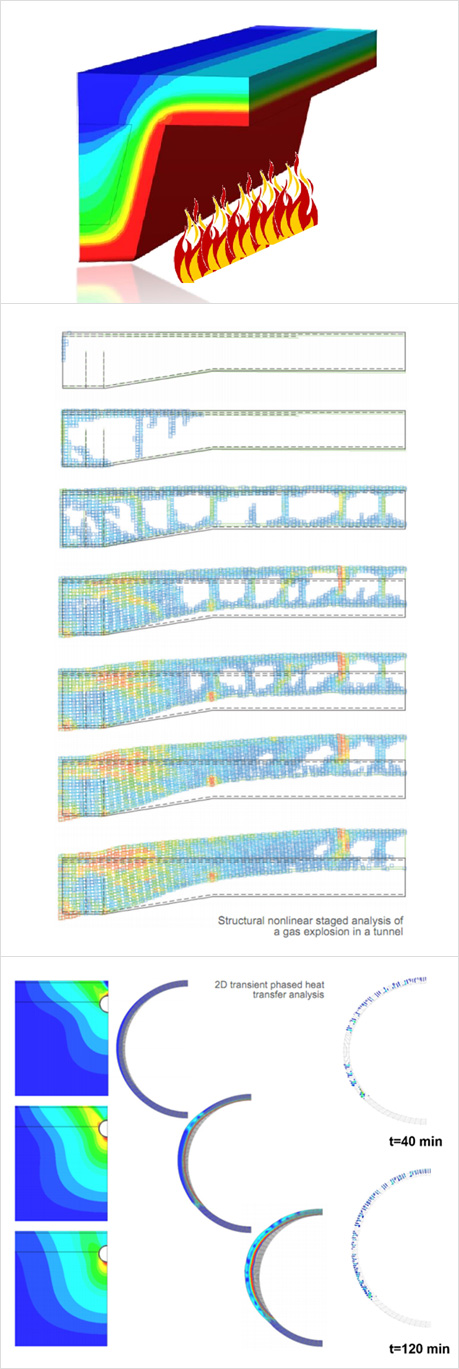
화재의 발생은 구조물의 기능손실 또는 붕괴를 야기합니다. 이로 인한 위험 요소로는 경제적 손실과 이보다 중요한 인명 피해가 주된 요소가 됩니다. 엔지니어들은 화재 시 대피할 수 있는 충분한 시간과 응급 서비스가 도착할 때까지의 시간을 확보해야 할 의무를 가지고 있습니다. 엔지니어들은 화재 안전 평가에 대한 규칙을 코드와 표준을 활용하여 고려할 수 있습니다. 그러나 이러한 규칙이 반드시 최적의 설계를 보장하지 않거나 또는 모든 구조물에 적용할 수 없는 경우도 있습니다. 이러한 경우 수치해석이 반드시 설계에 동반되어야 합니다.
화재가 발생하는 동안 구조물 내에는 열변형이 발생하고 이 변형은 역학적 하중, 크리프와 건조수축에 의한 변형에 합산됩니다. 또한 재료적 측면에서는 역학적 성질의 열화와 이로 인한 구조물의 손상(콘크리트 균열과 재료의 소성화)이 야기됩니다. DIANA는 예를 들어 지진과 같은 기존의 구조적 손상을 고려하여, 화재 시 구조적 거동을 평가하는 데 필요한 모든 분석 기능을 제공합니다.
화재해석 전용기능 (Dedicated Features for Fire Analysis) 해석 기능 (Analysis Features)- Coupled thermo-stress with automatic conversion of temperature field to mechanical loading
- Possibility to add/remove elements or change boundary conditions during the analysis
- Heat transfer by conduction, convection and radiation
- Temperature and time dependence of thermal material properties
- Boundary elements for environmental conditions
- Automatic changing to lower order elements from stress to flow analysis to guarantee strain compatibility from temperature field loads to stress analysis
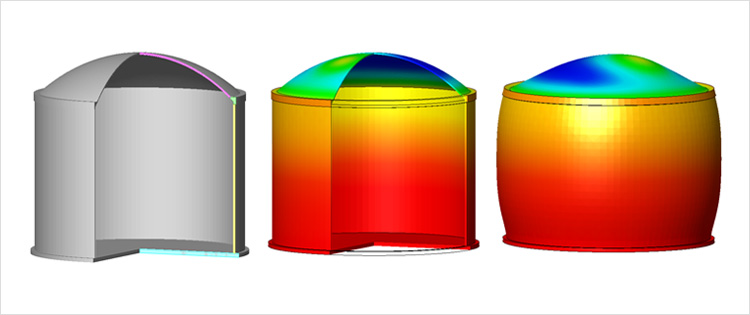
- Isotropic and orthotropic thermal expansion
- Isotropic elasticity with temperature dependent thermal expansion, Young’s modulus and Poisson’s ratio
- Isotropic plasticity with temperature dependent yield stress: Tresca and Von-Mises
- Isotropic plasticity with temperature dependent cohesion: Mohr-Coulomb and Drucker-Prager
-
Smeared crack models with:
- - Temperature dependence of the tension cut-off and tension softening
- - Temperature dependence of shear behavior
- - Temperature dependence of compression functions
- Discrete crack model with temperature dependence of the tension cut-off and tension softening
- Visco-elasticity with temperature dependent Young’s modulus: Power law, Kelvin and Maxwell chains
- Transient creep
- Temperature dependent shrinkage
- User-supplied subroutines