소프트웨어
건설분야 최고의 해석 솔루션 DIANA와 함께 합니다.
DIANA
Earthquake Engineering (지진공학)
인구 밀집 지역에 큰 지진이 발생한다면 엄청난 재앙이 발생할 수 있습니다. 지진은 쓰나미로 인한 물의 범람, 인접 구조물의 붕괴, 지반의 액상화 및 화재 등을 동반합니다.
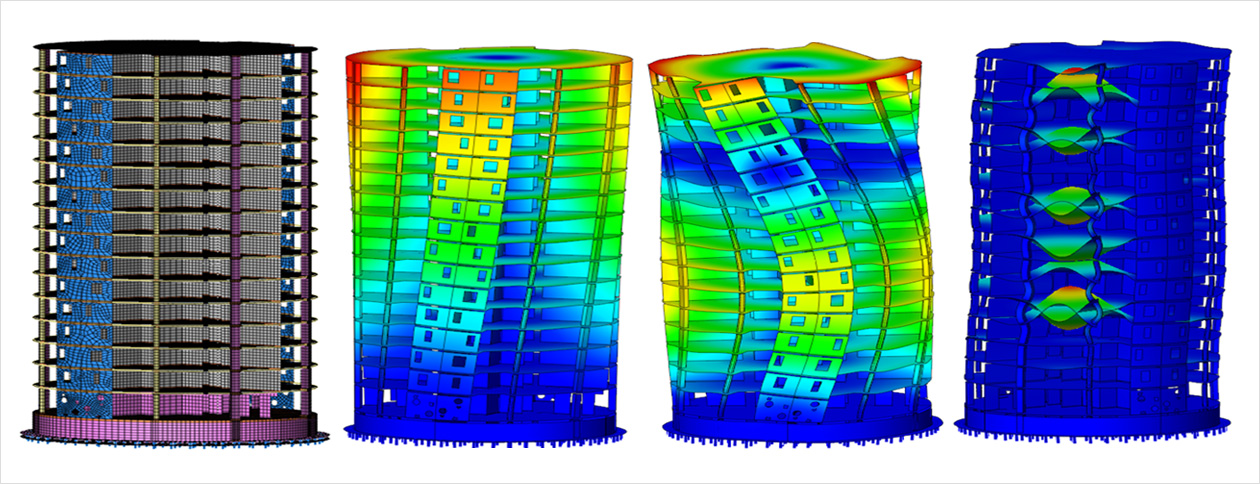
최근 지진 민감 지역에서 새롭게 건설되는 구조물은 내진설계를 통해 손상이나 붕괴없이 지진에 견디도록 설계되고 있습니다. 그러나 구조의 손상, 재료의 열화 또는 변경된 하중과 같이 구조물의 상태가 변경된 경우 내진에 대한 성능이 현저하게 감소할 수 있습니다.
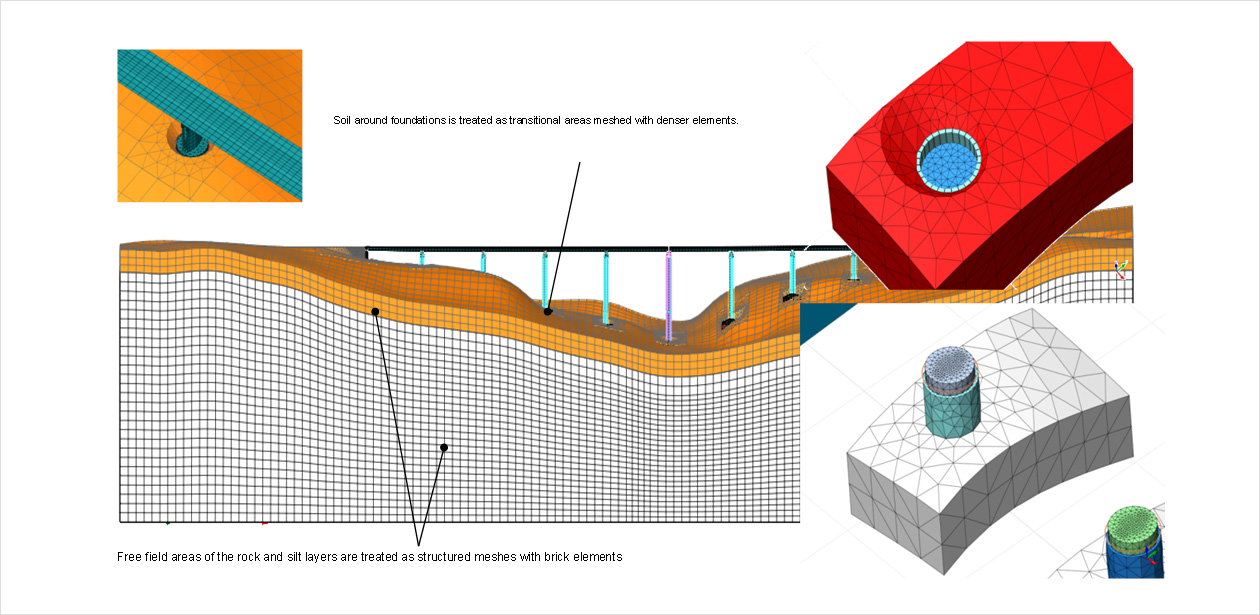
또한, 많은 비표준 구조의 내진설계는 동적 유한 요소 해석을 필요로 합니다. 간단한 평가를 위해 주파수 영역에서 선형 분석으로 충분할 수 있습니다. 그러나 보다 세밀한 평가의 경우 파괴 메커니즘을 고려한 비선형 특성과 구조물과 지반 및 주변 환경과의 상호 작용을 비선형 시간이력해석과 연동하여 고려해야 합니다.
DIANA는 구조물 설계에 적용 할 수 있는 간단한 선형 동적 해석과 구조의 하중 이력을 고려한 완전한 비선형 동적 해석을 위한 솔루션을 제공합니다.
지진 공학 전용기능 (Dedicated Features for Earthquake Analysis)
지진해석의 형태 (Type of Earthquake Analysis)
- Linear transient analysis with different time integration schemes
- Direct frequency response analysis
- Modal response analysis
- Spectral response analysis
- Nonlinear transient analysis with different time integration schemes
- Hybrid frequency-time domain analysis
- Pushover load & pushover analysis
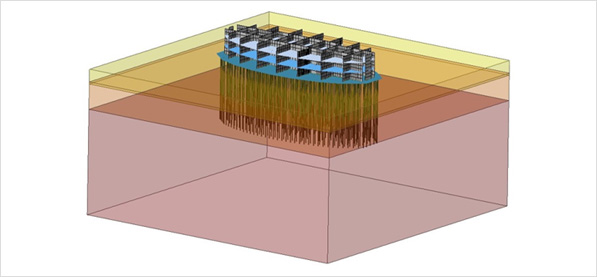
모든 동적 해석은 유체-구조 상호 작용 효과와 함께 사용할 수 있습니다. 유체 - 구조 경계면에서 완전 연계된 가속도-압력 행렬이 경계면 상의 정상 변위에 대해 계산됩니다. 이 상호작용 행렬은 구조 해석에서 유체의 움직임이 구조에 미치는 영향을 설명합니다. 주파수 종속 효과는(유체 압축성 및 경계 감쇠와 같은) 다양한 해석 형태로 정의 할 수 있습니다.
요소 타입 (Element Types)
동해석에는 모든 형태의 구조요소가 사용될 수 있습니다.
질량과 감쇠 (Mass and Damping)- Mass density per unit volume
- Reduced mass density for dead weight correction
- Distributed mass elements with damping properties for defining non-reflection boundaries
- Consistent and lumped concentrated translational masses and rotational inertia
- Viscous or Rayleigh damping
- Structural or hysteretic damping
- Continuous damping via discrete spring/dashpot elements
- Base excitations, single and multi-directional
- Prescribed nodal accelerations (2011) and displacements
- Time-load diagrams, e.g. accelerograms
- Frequency-load diagrams, e.g. spectra
- Specified initial displacement and/or velocity fields
- Initial stresses
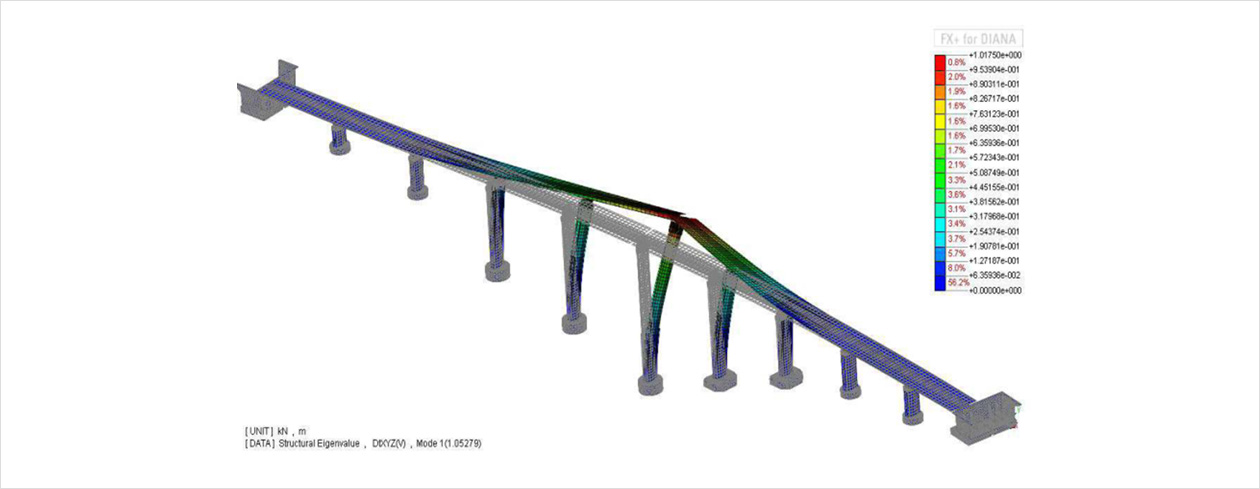
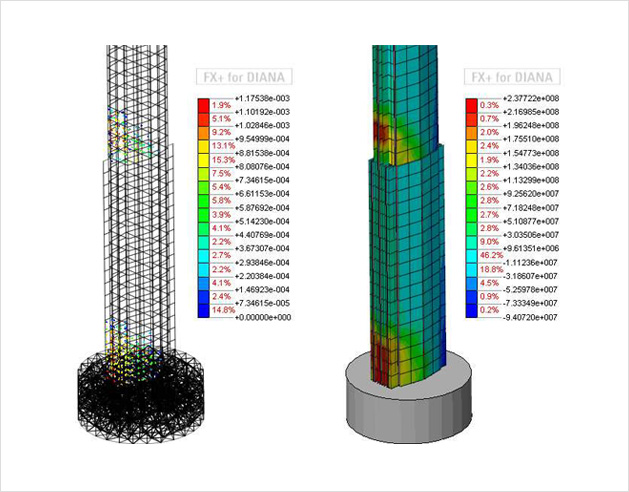

- Possibility to add stress-stiffness to linear elastic stiffness matrix in frequency analysis
- For direct Frequency Response output of complex results and/or amplitude-phase results
- Lanczos Eigensolver withvarious decomposition techniques, shifting option, and automatic ordering
- Spectral Response with ABS, SRSS, and CQC output
- Euler backward, Newmark, Wilson-theta, Hilber-Hughes-Taylor, and Runge-Kutta time-integration
- Total-strain cracking models
- Modified Maekawa-Fukuura concrete model ( Multi-Axial Damage and Cracked Concrete models)
- Monti-Nuti-steel model
- Modified 2-surface steel model
- Hardin-Drnevich and Ramberg-Osgood simple soil models
- UBC, Bowl, Nishi and Towhata-Iai liquefaction models
- Engineering liquefaction analysis
